Guide to Stainless Steel 3D Printing[+Free Cost Calculator]

This informative article serves as both a knowledge guide to stainless steel 3D printing and a buying guide to help customers select the most suitable service provider.
Introduction
Stainless Steel (SS) is known for its strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, making it ideal for aerospace, medical, automotive, and consumer applications.
With recent advancements in manufacturing, 3D printing has revolutionized SS fabrication, offering greater design flexibility, reduced waste, and the precise production of complex parts.
Understanding 3D Printing Stainless Steel
Stainless steel 3D printing has become one of the most advanced and reliable methods for producing high-performance metal parts across multiple industries. By combining the precision of digital design with the strength and durability of stainless steel, additive manufacturing (AM) enables engineers to create complex geometries that were once impossible using traditional techniques.
DMLS/SLM, Binder Jetting (BJ), and Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and are common technologies used to 3D print stainless steel parts.
Stainless steel is widely applied across a variety of fields, from aerospace and automotive to healthcare and consumer products, thanks to its strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility.
Basics of Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing (AM), also known as 3D printing, builds objects layer by layer from a digital design. For stainless steel, this typically involves a metal powder and a high-powered laser. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Powder Preparation: Fine stainless steel powder is spread onto a platform.
Laser Melting: A high-powered laser selectively melts the powder particles according to the design blueprint.
Layer by Layer: The platform lowers, and a new layer of powder is deposited. The laser then melts the fresh powder, fusing it to the previous layer.
Support Removal: Once complete, the part is removed from the machine, and any support structures used during printing are removed.
Advantages of 3D Printing Over Traditional Methods in Making Stainless Steel Parts
Compared with traditional methods like casting, molding and machining, 3d printing has several unique advantages in making stainless steel parts as follows:
Design Freedom
Traditional manufacturing limits complexity. 3D printing enables intricate geometries, internal channels, and lightweight structures without extra cost.
Faster Production
No need for molds or setups—get functional stainless steel parts in days, perfect for rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
Cost-Effective for Low to Medium Volumes
No tooling costs, making 3D printing affordable for prototypes, custom parts, and limited production runs.
Minimal Material Waste
Uses only the necessary material, reducing scrap compared to machining.
Strong, Integrated Parts
Fewer weak points—complex assemblies can be printed as a single durable component.
On-Demand Manufacturing
No need for large inventories—print only what you need, when you need it.
Typical Applications of Stainless Steel 3D Printing
Stainless steel 3D printing is transforming the way industries design and manufacture metal parts. Its unique combination of strength, durability, and design flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications.
In the following sections, we’ll highlight the key industries where stainless steel 3D printing is making the biggest impact and explain why it is so widely adopted.
1. Aerospace & Automotive
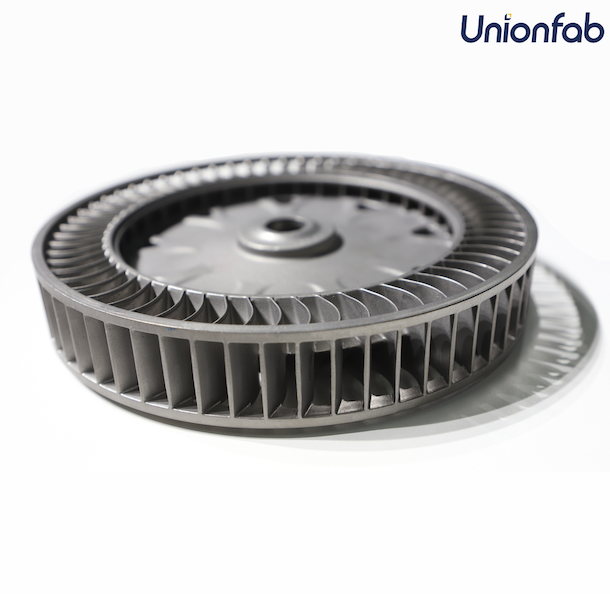

Key Properties: High strength-to-weight ratio, temperature and corrosion resistance.
Applications:
Aerospace: Engine components (turbine blades, fuel nozzles), structural parts (brackets, mounts), tooling (jigs, fixtures).
Automotive: Engine and exhaust components (manifolds, valves), custom parts (brackets, connectors), prototyping.
Why It’s Suitable: Stainless steel's strength and heat resistance are essential in both aerospace and automotive industries. 3D printing allows for the creation of intricate, lightweight designs, rapid prototyping, and reduced production costs.
2. Medical & Healthcare
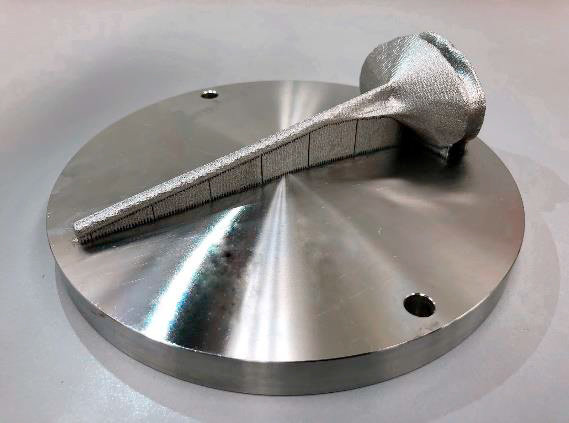

Source: researchgate.com
Key Properties: Biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, ease of fabrication.
Applications:
Medical Devices: Surgical instruments (scalpels, forceps), implants (orthopedic implants, dental crowns), diagnostic equipment components.
Why It’s Suitable: 316L stainless steel's biocompatibility and corrosion resistance make it ideal for medical applications. 3D printing provides the flexibility to create custom, patient-specific devices efficiently.
3. Oil, Gas & Industrial Manufacturing
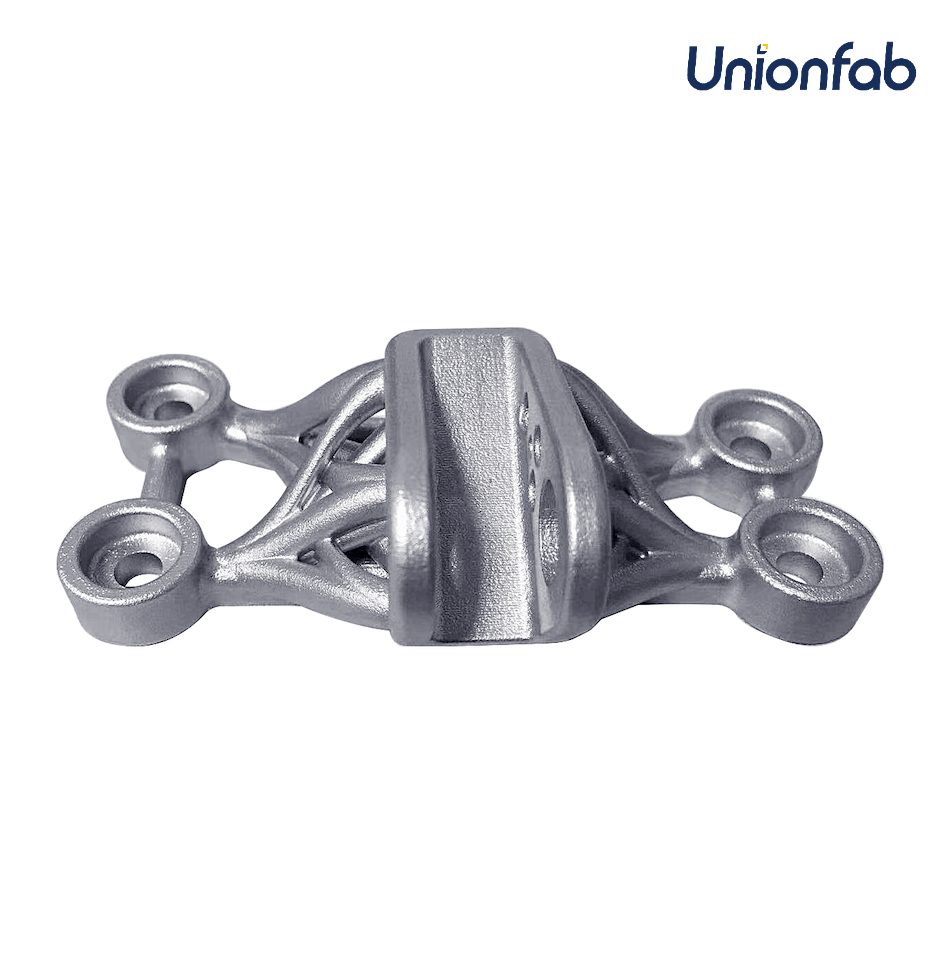

Key Properties: Corrosion resistance, strength, wear resistance.
Applications:
Oil & Gas: Drilling equipment (valves, pumps), pipeline components (fittings, connectors), tooling (wear-resistant tools).
Industrial Manufacturing: Machinery components (gears, bearings), tooling (molds, jigs), wear-resistant parts (conveyor belts, cutting tools).
Why It’s Suitable: Stainless steel's durability in harsh environments ensures reliability in oil, gas, and industrial manufacturing. 3D printing enables the production of custom parts on-demand, improving efficiency, reducing downtime, and cutting inventory costs.
4. Food, Beverage & Consumer Goods
Key Properties: Corrosion resistance, ease of cleaning, strength.
Applications:
Food & Beverage: Processing equipment (mixers, conveyors), custom fixtures (nozzles, molds), tooling (maintenance parts).
Consumer Goods: Wearables (watch cases, jewelry), electronics housings (custom enclosures), custom tools (household gadgets).
Why It’s Suitable: Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion, ease of cleaning, and aesthetic appeal make it ideal for both food-grade applications and consumer goods. 3D printing allows for the rapid creation of custom components with high precision.
Materials Comparison: Stainless Steel 316L vs. 17-4 PH vs. 304L vs. 15-5 PH
After understanding the advantages of 3D printing for stainless steel, the next step is choosing the right material for your specific application. In 3D printing, some of the most commonly used stainless steels include 316L, 17-4 PH, 304L, and 15-5 PH. Below is a comparison of these materials to help you make an informed decision.
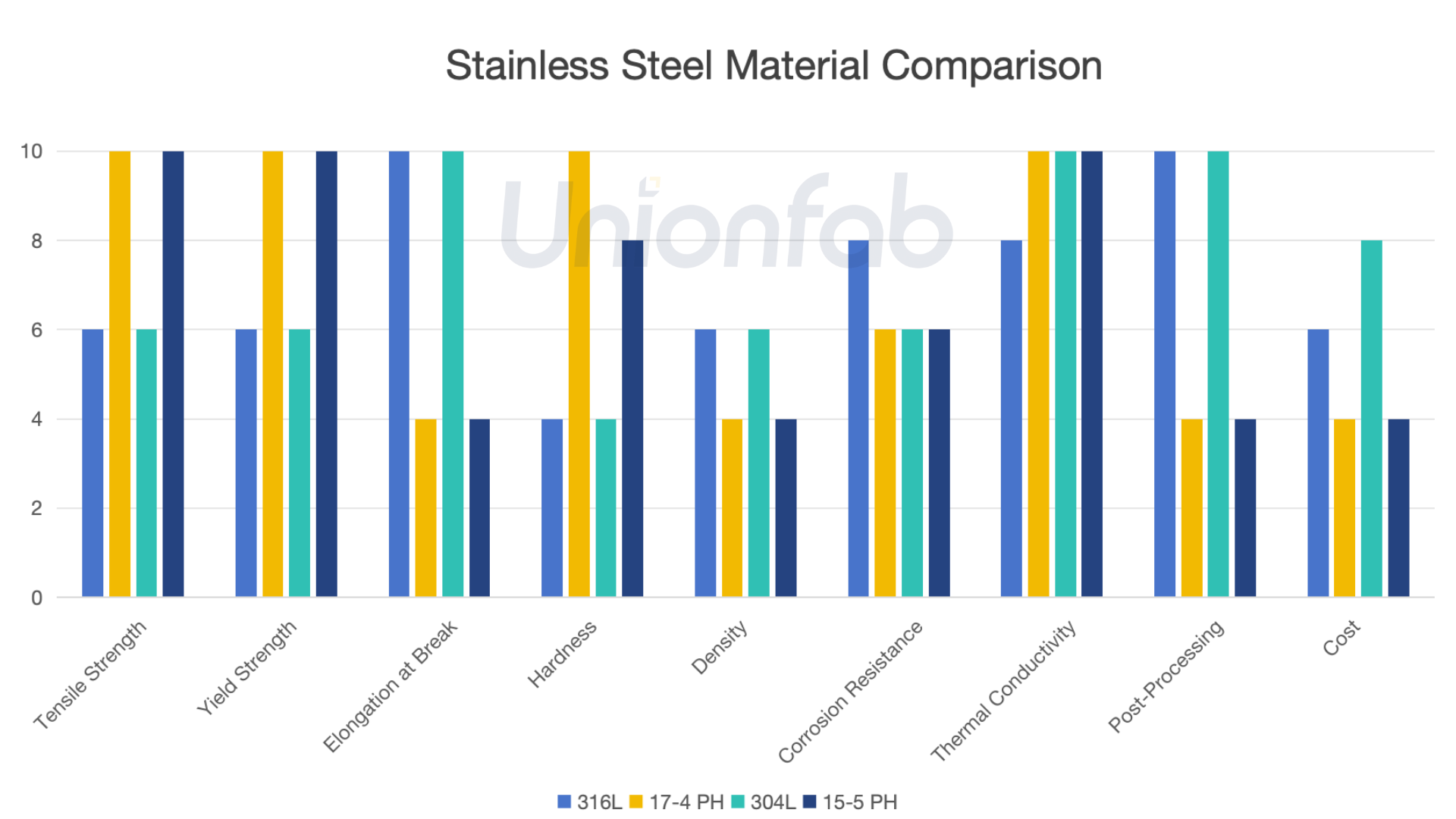
To provide a clearer visual representation, here’s a bar chart comparing the key properties of these materials.
Since higher scores indicate better performance in each category, materials with higher scores in tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity are considered superior. Similarly, higher scores in the post-processing difficulty and cost categories also mean lower corresponding difficulty and cost, reflecting better overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Next, let's take a look at a table that provides a more detailed comparison of the key properties of each material.
Property | 304L | 15-5 PH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Tensile Strength (MPa) | 485–620 | 1000–1200 | 485–620 | 1000–1100 |
Yield Strength (MPa) | 170–310 | 850–1000 | 170–310 | 860–1050 |
Elongation | 40–50 | 10–20 | 40–45 | 10–20 |
Hardness (Brinell) | 146–190 | 330–400 | 146–190 | 330–370 |
Density (g/cm³) | 7.9 | 7.75 | 7.9 | 7.75 |
Corrosion Resistance | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
Thermal Conductivity | 15–16 | 16–17 | 16.2 | 16–17 |
Post-Processing | Stress relieving | Solution treatment & aging | Stress relieving | Solution treatment & aging |
Cost | $$ | $$$ | $ | $$$ |
Key Takeaways:
Mechanical Properties: 17-4 PH and 15-5 PH have higher strength but lower ductility than 316L and 304L.
Corrosion Resistance: 316L excels in chloride environments, while the others offer good but lower resistance.
Thermal Properties: All grades have similar thermal conductivity.
Density: 316L and 304L are slightly denser than 17-4 PH and 15-5 PH.
Post-Processing: 17-4 PH and 15-5 PH require solution treatment and aging, while 316L and 304L need stress relieving.
Cost: 304L is the cheapest, 316L is moderate, and 17-4 PH and 15-5 PH are the most expensive.
How Do Stainless Steel 3D Printing Technologies Work?
The main technologies used in stainless steel 3D printing include Selective Laser Melting (SLM) / Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Binder Jetting (BJ), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), Direct Energy Deposition (DED), Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM), and Cold Spray.
Among these, SLM/DMLS, BJ, and EBM are the most commonly used, as they are the most mature processes, deliver consistently high-quality parts, and have the widest range of applications across industries.
In the following sections, we will take a closer look at how each of these technologies works.
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) / Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
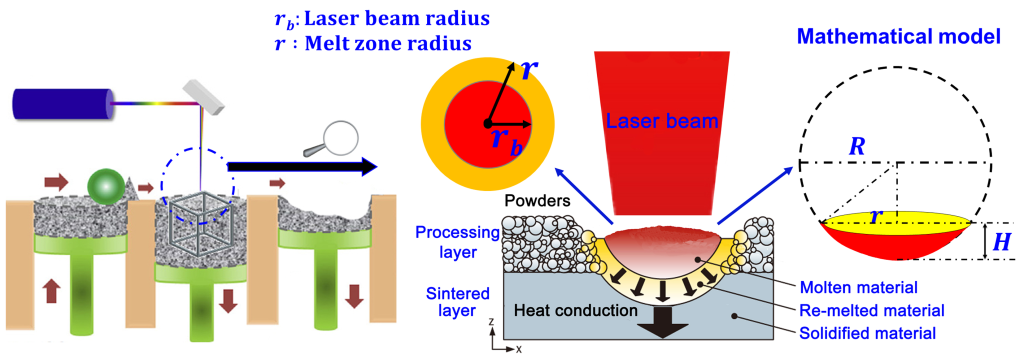
Source: wikipedia.org
SLM, also known as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), is the most widely used technique for 3D printing stainless steel. Its process involves using a high-powered laser to melt metal powder and build parts layer by layer.
1. Powder Layering
A thin layer of metal powder is spread evenly across the build platform.
2. Laser Sintering
A high-powered laser selectively melts the metal powder based on the design file, fusing the particles together.
3. Layer-by-Layer Construction
The build platform lowers slightly, and a new layer of powder is applied. The laser then melts the fresh powder, bonding it to the previous layer.
4. Cooling and Solidification
Each melted layer solidifies as it cools, creating a strong bond with the layer beneath it.
Binder Jetting (BJ)
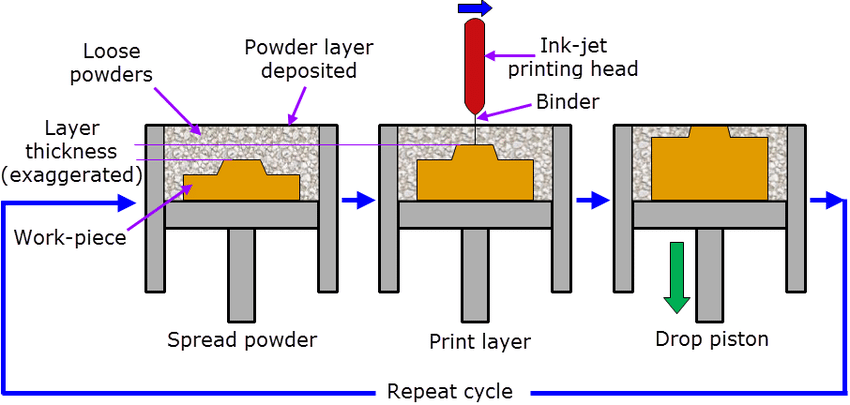
Source: oceanproperty.co.th
Binder Jetting uses a binder solution to selectively adhere metal powder particles together.
1. Powder Spreading
A layer of metal powder is evenly spread across the build platform.
2. Binder Application
A print head jets a liquid binder onto the specific areas of the powder bed, adhering the powder particles together to form the part layer.
3. Layer-by-Layer Building
After the binder is applied, a new layer of powder is spread, and the process repeats for each layer.
4. Sintering
The "green part" is placed in a furnace, where it is sintered, causing the binder to burn off and the metal powder to fuse into a solid form.
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Uses an electron beam to melt metal powder layer by layer in a vacuum chamber. It is similar to SLM, but uses an electron beam instead of a laser.
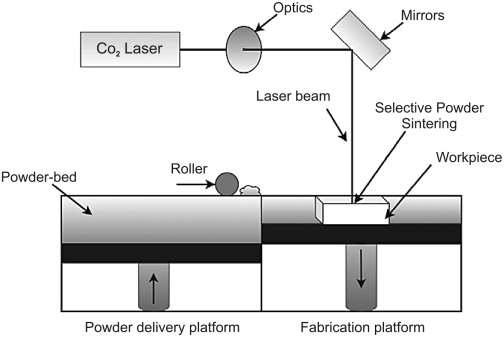
Source: 3dprintingindustry.com
EBM uses an electron beam to melt metal powder layer by layer in a vacuum.
1. Powder Spreading
A thin layer of metal powder is spread across the build platform within a vacuum chamber.
2. Electron Beam Melting
A focused electron beam is directed at the powder to melt it, following the path of the 3D model.
3. Layer-by-Layer Construction
After each layer is melted, the platform lowers slightly, and a new layer of powder is spread and melted by the electron beam.
4. Cooling and Solidification
The molten powder solidifies as it cools, bonding to the previous layer.
Direct Energy Deposition (DED)
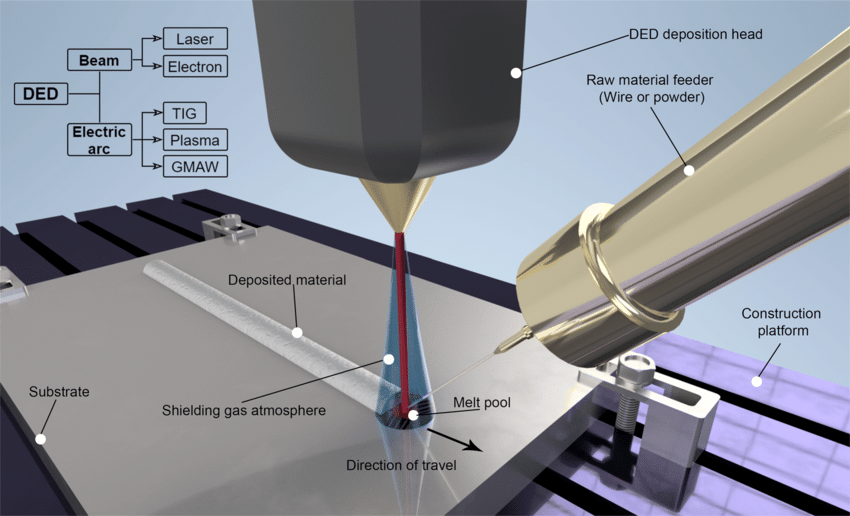
Source: additec3d.com
DED uses a focused energy source to melt metal powder or wire and deposit it directly onto a substrate.
1. Material Feeding
Metal powder or wire is fed into the melt pool created by a laser, electron beam, or plasma arc.
2. Deposition
The material is melted by the energy source and deposited directly onto the substrate, layer by layer.
3. Layer-by-Layer Construction
The substrate moves, and new material is added to the melt pool, building the part layer by layer.
4. Cooling and Solidification
The molten material solidifies, fusing with the underlying layers.
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)
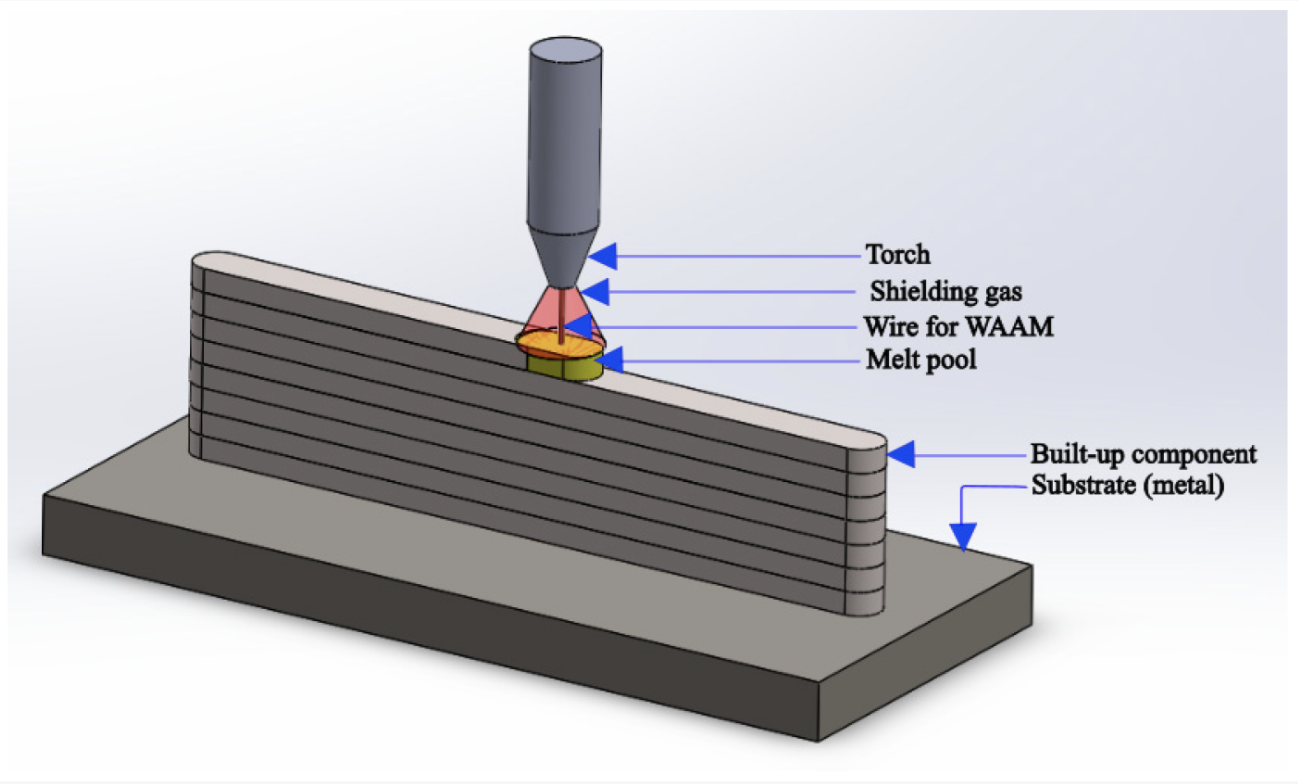
Source: mdpi.com
WAAM uses an electric arc to melt a metal wire and deposit it layer by layer.
1. Wire Feeding
A metal wire is continuously fed into an electric arc, which melts the wire.
2. Deposition
The melted metal is deposited onto the substrate, forming one layer at a time.
3. Layer-by-Layer Construction
The wire continues to feed into the arc, and the part is built layer by layer.
4. Cooling and Solidification
The molten metal cools rapidly and solidifies, bonding to the previous layer.
Cold Spray
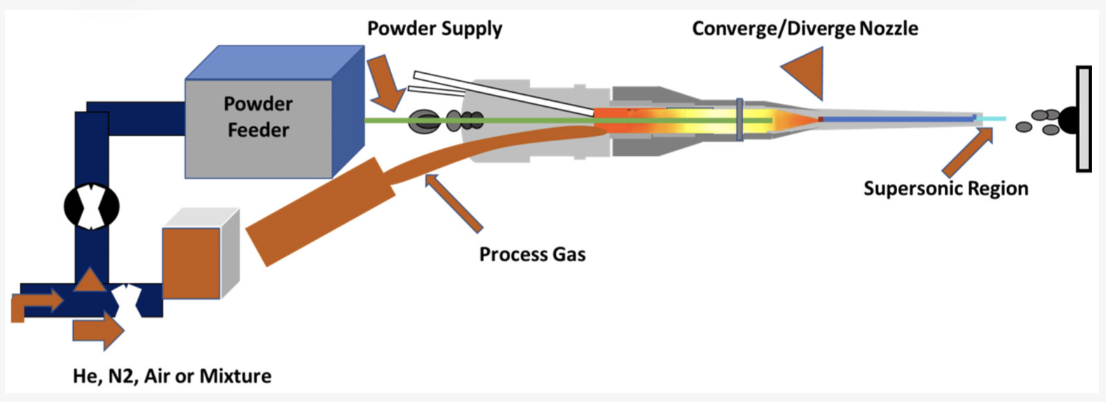
Source: mdpi.com
Cold Spray uses high-pressure gas to accelerate metal powder particles and bond them to a substrate without melting.
1. Powder Acceleration
Metal powder is accelerated using high-pressure gas to supersonic speeds.
2. Impact and Bonding
The accelerated powder particles impact the substrate and bond mechanically without melting.
3. Surface Coating
The process is ideal for applying coatings or adding material to existing parts.
4. Cooling
As no melting occurs, there is minimal thermal distortion, and the substrate remains relatively cool.
Technology Comparison: SLM/DMLS vs. BJ vs. EBM vs. DED vs. WAAM vs. Cold Spray
In this section, we’ll compare six key 3D printing technologies—SLM, BJ, EBM, DED, WAAM, and Cold Spray—for stainless steel applications. To help visualize their differences, let's first take a look at a bar chart that highlights their performance across several key dimensions.
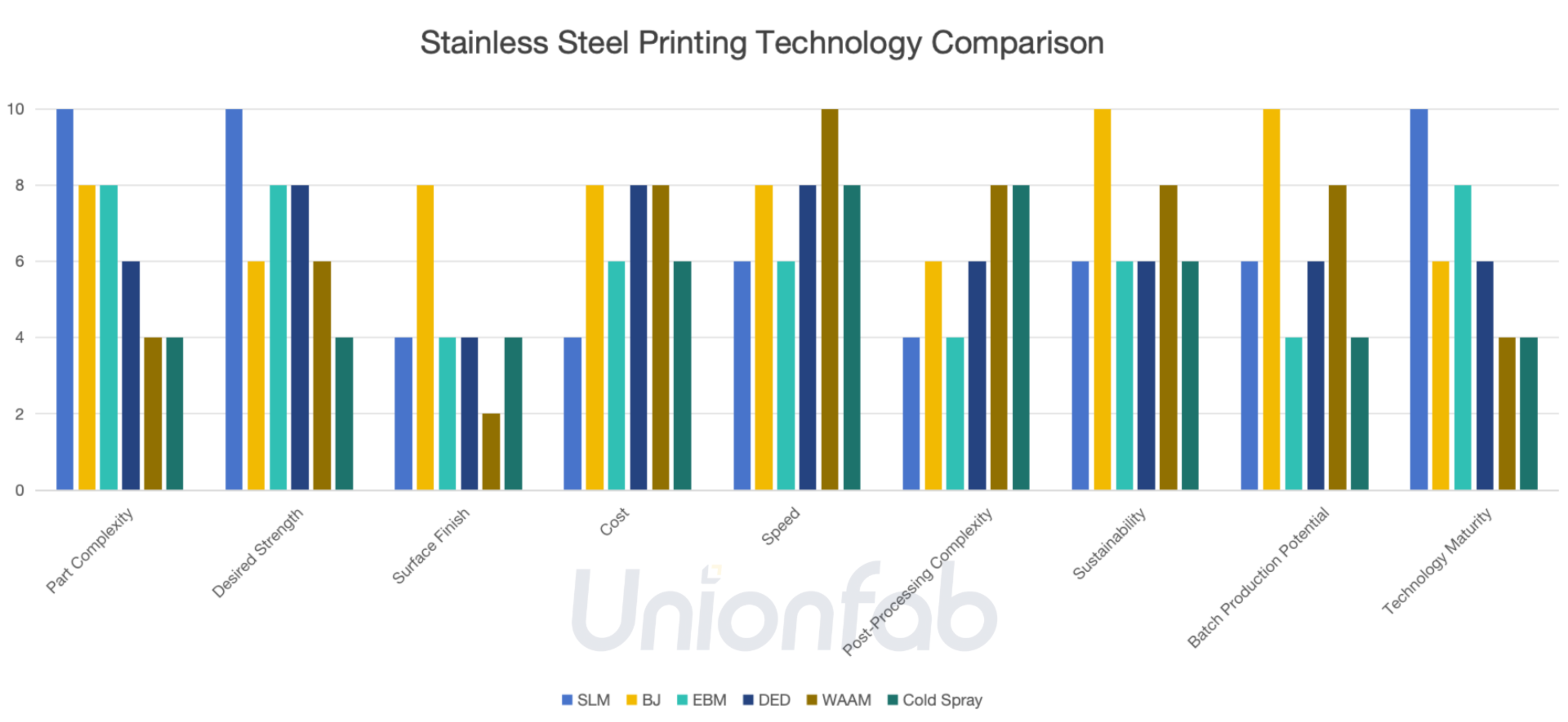
As shown in the chart, each technology offers distinct advantages and trade-offs. Next, we’ll break down these differences in more detail with a comprehensive table, comparing their characteristics across various categories.
Dimension | SLM | BJ | EBM | DED | WAAM | Cold Spray |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Part Complexity | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
Desired Strength | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
Surface Finish | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
Cost | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
Speed | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Post-Processing Complexity | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
Sustain-ability | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
Batch Production Potential | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
Technology Maturity | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ |
Key Takeaways
SLM: Best for high-strength, complex parts with tight tolerances (e.g., medical implants).
Binder Jetting: Optimal for low-cost, high-volume production of less critical parts.
EBM: Balances strength and high-temperature performance (e.g., aerospace components).
DED: Best for repairing, large parts, and functional components that require high strength and fast deposition, but with lower surface finish and precision.
WAAM: Ideal for large, low-cost structures where surface finish is secondary.
Cold Spray: Specialized for repairs, coatings, or hybrid manufacturing.
Cost-saving Design Tips
Here are some practical design tips to help you save on costs while maintaining strength and precision in your stainless steel prints.
1.Optimize Wall Thickness
● Avoid Excessive Thickness: Keep walls at 1-2 mm to reduce material usage and printing time.
● Uniform Thickness: Ensure consistent thickness to prevent warping or stress.
2.Minimize Support Structures
● Design Self-Supporting Geometries: Use angles >45 degrees to reduce support material and labor.
● Hollow Structures: Use hollow or lattice designs to save material while maintaining strength.
3.Simplify Complex Features
● Reduce Overhangs/Undercuts: Simplify designs to minimize additional supports and post-processing.
● Combine Parts: Print assemblies as a single part to cut fasteners and assembly time.
4.Use Tolerances Wisely
● Avoid Tight Tolerances: Use standard tolerances to reduce printing time and avoid extra machining.
● Account for Shrinkage: Design with shrinkage in mind to avoid reprints.
5.Reduce Post-Processing Needs
● Smooth Surfaces: Design with smooth transitions to minimize sanding or polishing.
● Avoid Small Features: Simplify intricate details to reduce finishing work.
6.Leverage Software Tools
● Topology Optimization: Remove unnecessary material while maintaining strength, resulting in lighter, cost-effective parts.
● Simulation Software: Use tools like finite element analysis (FEA) to test and optimize designs before printing, reducing failure risks.
If you want to calculate the 3d printing cost of your model, Unionfab’s free cost calculator is a good helper.
Post-processing Techniques for 3D Printed Stainless Steel
After 3D printing stainless steel parts, post-processing is often required to improve their mechanical properties and surface finish. Below are the most common post-processing techniques used for stainless steel 3D prints:
1. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is crucial for relieving internal stresses and enhancing the material's strength. This step is especially important for parts that need to endure high temperatures or heavy loads. Common types of heat treatment include annealing and tempering.
2. Surface Finishing
The surface finish of 3D printed parts can be rough, so surface finishing methods like bead blasting are often used to smooth the part's surface. This not only improves the part's aesthetic quality but also its functional performance in specific applications.
3. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) (Optional)
HIP is an optional post-processing method that can further enhance the quality of 3D printed stainless steel parts. By applying high pressure and temperature, HIP helps to eliminate any residual porosity, improving the part's density and mechanical properties. This process is particularly useful for parts that require maximum strength and are intended for high-performance applications.
By incorporating these essential post-processing techniques, you can significantly enhance the quality and performance of your stainless steel 3D prints, making them suitable for a wide range of demanding applications.
For more details on post-processing, check out our dedicated post-processing guide.
Comparison of Key Stainless Steel 3D Printing Service Providers
To help you choose the most suitable service provider based on your needs, we have listed a table to compare several key stainless steel 3D printing service providers as follows.
Service Provider | One-line Profile | Technology | Material | Max. Build Volume | Online Instant Quoting System | *Sample Cost | Lead Time(Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Xometry | A US-based Global Factory-less 3D Printing Supply Chain Platform | SLM/DMLS, Binder Jetting | SLM/DMLS: Stainless Steel 17-4PH, Stainless Steel 316L Binder Jetting: Stainless Steel 316L | SLM/DMLS: 250 x 250 x 250 mm Binder Jetting: 400 x 250 x 250 mm | ✅ | $575.26 | 10 |
Shapeways | A US-based Global Factory-less 3D Printing Supply Chain Platform | Binder Jetting | Stainless Steel 17-4PH, Stainless Steel 316L | 127 x 127 x 76.2 mm | ❌ | / | / |
Unionfab | A China-based Global 3D Printing Service Provider with Six In-house Factories | SLM/DMLS, Binder Jetting | SLM/DMLS: Stainless Steel 316L, Stainless Steel 17-4PH Binder Jetting: Stainless Steel 316L, Stainless Steel 17-4PH | SLM/DMLS: 400 x 300 x 400 mm Binder Jetting: 400 × 250 × 250 mm | ✅ | $45.49 | 4-5 |
Facfox | A China-based Global Factory-less 3D Printing Supply Chain Platform | SLM/DMLS, Binder Jetting | SLM/DMLS: Stainless Steel 316L, Stainless Steel 17-4PH Binder Jetting: CJP Fullcolor Sandstone | SLM/DMLS: 500 x 500 x 1000 mm Binder Jetting: 254 x 381 x 203 mm | ✅ | $46.93 | 8 |
Materialise | A Belgium-based 3D Printing Company | SLM/DMLS | Stainless Steel 316L | 500 x 280 x 315 mm | ✅ | $272.39 | 11 |
Additive3dasia | A Singapore-based 3D Printing Company | SLM/DMLS | Stainless Steel 316L | Not Mention | ❌ | / | / |
Ram3d | A New-Zealand-based 3D Printing Company | SLM/DMLS | Stainless Steel 316L, Stainless Steel 15-5ph | Not Mention | ❌ | / | / |
*Note: The sample cost is calculated via the online instant quoating systems of each company above.
Volume: 74.62cm³; Mateial: Stainless Steel 316L; Tech: Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
In summary,
Xometry, Unionfab and Facfox provide both SLM and Binder Jetting technologies, as well as richer materials compared to others competitors.
Facfox provides the largest build volume using SLM, while Xometry and Unionfab provide the largest build volume using Binder Jetting.
Case Study: Stainless Steel Face Mask Mold by Unionfab
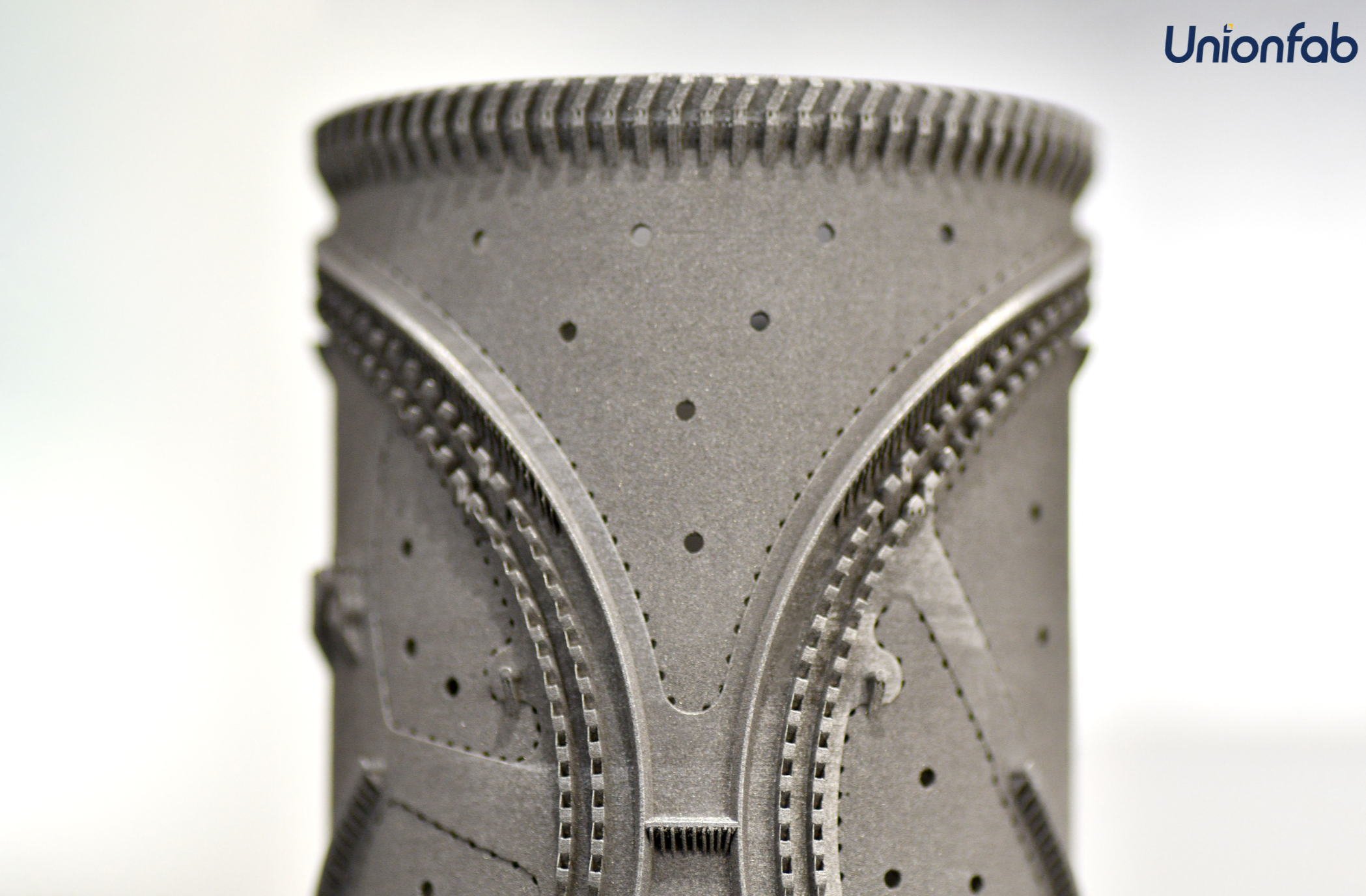

Unionfab utilized Selective Laser Melting (SLM) technology to manufacture a highly accurate Stainless Steel 316L mold for N95 masks.
This mold enabled the fast and efficient large-scale production of protective masks, contributing to public health efforts during crucial times.
Key Details:
● Material: Stainless Steel 316L
● Size: 79mm * 140mm
● Machine Time: 15 hours
Why 3D Printing?
Traditionally, rotary die molds face several challenges—high manufacturing costs, long production cycles, and a significant amount of material waste. By using SLM 3D printing, we were able to address these issues effectively. Here’s how:
● Complex Geometry, Simplified: The mold's design features intricate details that would have been difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. 3D printing enabled us to create a complex, lightweight structure without compromising on precision.
● Faster Production: Using 3D printing drastically reduced the time it would take to produce the mold, from weeks down to just three days. This not only accelerated the project but also allowed for quick iterations if needed.
● Durability and Performance: Stainless Steel 316L was the material of choice due to its corrosion resistance and high strength, ensuring the mold would endure heavy use and maintain its performance over time.
The Result?
The final 3D printed N95 mask mold was both lightweight and precise, providing an excellent solution for the production of mask components. With SLM 3D printing, Unionfab was able to produce a high-quality, durable mold in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods, meeting the customer's needs for both speed and performance.
Unionfab's Stainless Steel 3D Printing Service
With 20+ years of expertise, 1,000+ industrial 3D printers, and 6 cutting-edge factories, Unionfab, certified with ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and AS 9001D, is committed to delivering high-quality, cost-effective 3D printing services. The followings are the details of our stainless steel 3d printing service.
SLM/DMLS | Binder Jetting | |
|---|---|---|
Equipment | 100+: BLT; SLM; EOS; EXONE | 10+: HP S100 |
Materials | Stainless Steel 316L, Stainless Steel 17-4PH | Stainless Steel 316L, Stainless Steel 17-4PH |
Max Part Size | 400 x 300 x 400mm | 400 × 250 × 250mm |
Layer Thickness | 0.035 mm | 0.05 mm |
Tolerance | ±0.2 mm | ±0.3 mm |
Min. Wall Thickness | 0.5 mm | 2.0 mm |
*Min. Reference Unit Price | SS 316L: $0.4/g | SS 316L: $0.4/g |
Pass Rate | 99.5% | 99.5% |
Lead Time | As fast as 4-5 days | As fast as 4-5 days |
On-time Delivery Rate | 98% | 98% |
*The actual unit price is subject to real-time inquiry.
Post Processing
We not only provide cost-effective stainless steel 3d printing but also a range of post-processing options below, including sandblasting, electroplating, and polishing etc., to improve surface quality, durability, and aesthetics of the prints, ensuring the perfect fit for your diverse needs.

| 
| 
| 
| 
|
|---|---|---|---|---|

| 
| 
| 
| 
|

| 
| 
| 
| 
|
QA Report
In addition to delivering cost-effective prints, we also offer quality assurance services and can send the QA report with the shipment. Btw, if you haven’t used Unionfab’s 3d printing service yet, sign up now to get a 10% discount on your first order!
Customer Feedback
Here’s what customers are saying about Unionfab on Trustpilot:
Customer | Feedback |
|---|---|
Brem from US | ★★★★★ Surprised by the Low Price, but glad I took the risk. I was surprised and put off by the extremely low prices, and sometimes the offers of free parts, but I thought it was worth trying $20 at Unionfab, and I was not disappointed. I did their metal 3D printing service and I got my part super quick, I am looking to CNC some parts in the future and will use Unionfab for it most likely! Better customer service than most American companies, and cheaper too. |
Customer from JP | ★★★★★ This was my second time using it. As with the first time, I am very satisfied with the unit price and delivery date. Regarding the delivery date, it was very speedy and helpful. I would like to use it again in the future. |
Sean. S from US | ★★★★★ Trustworthy. The price of my 3D print was very competitive. Arrived about 10 days after submitting the 3D file (from China). The prints were high detail resin, and I'm very satisfied with the quality. Will definitely have them print more in the near future. Sent via UPS with tracking. |
Customer from JP | ★★★★ It was almost perfect. It was almost perfect and didn't have any issues on products. It was absolutely perfect if I can use OCS express to ship to Japan because their airfare cost is quite reasonable (cheap ship to Japan). |
Printed Online from FR | ★★★★★ Très professionnel Très professionnel, à l'écoute et réactif. Je recommande! |
UK_customer from GB | ★★★★★ Reliable. Multiple transactions - fast, reliable, great communication. |

